Hyundai Equus: Description and Operation
Hyundai Equus: Description and Operation
Second generation VI (2009–2025) / Hyundai Equus VI 2009-2025 Service Manual / Brake System / ESP(Electronic Stability Program) System / Description and Operation
| Description of ESP |
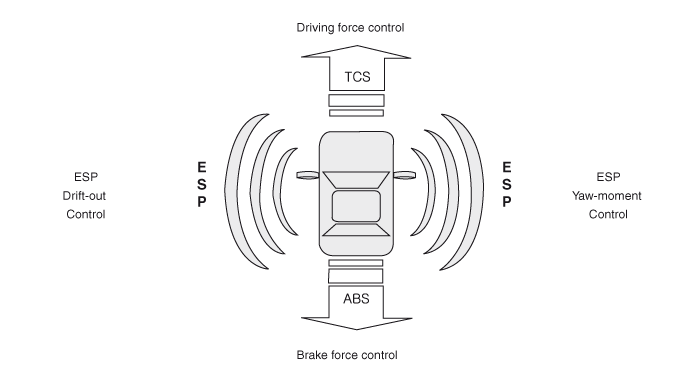
Optimum driving safety now has a name: ESP, the Electronic Stability Program.
ESP recognizes critical driving conditions, such as panic
reactions in dangerous situations, and stabilizes the vehicle by
wheel-individual braking and engine control intervention.
ESP adds a further function known as Active Yaw Control (AYC)
to the ABS, TCS, EBD and EDC functions. Whereas the ABS/TCS function
controls wheel slip during braking and acceleration and, thus, mainly
intervenes in the longitudinal dynamics of the vehicle, active yaw
control stabilizes the vehicle about its vertical axis.
This is achieved by wheel individual brake intervention and
adaptation of the momentary engine torque with no need for any action to
be taken by the driver.
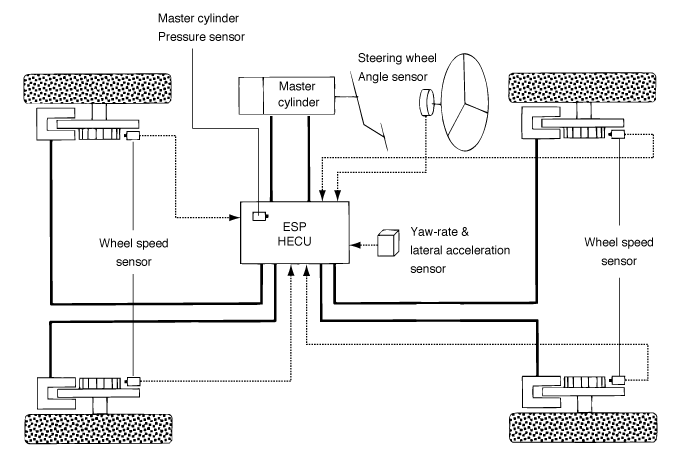
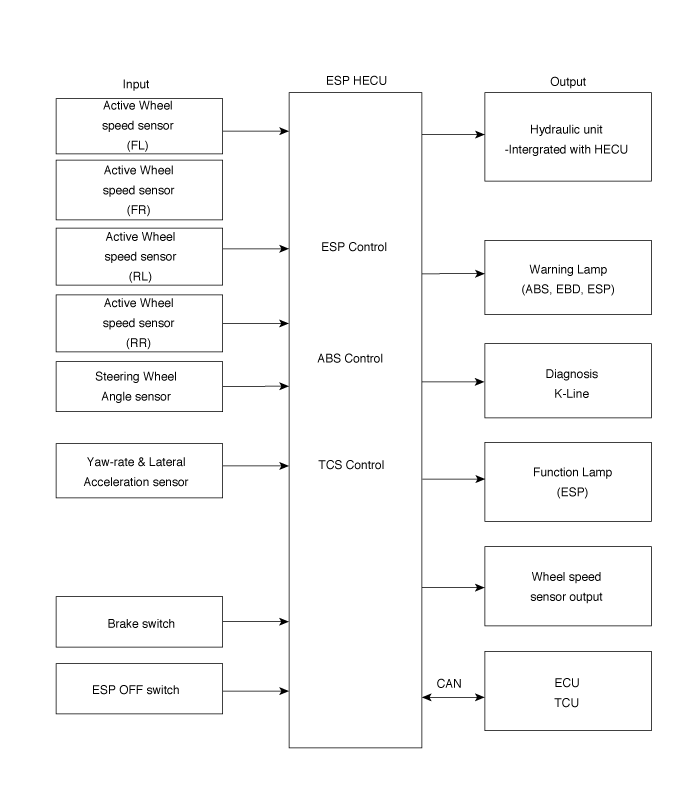
ESP essentially consists of three assemblies: the sensors, the electronic control unit and the actuators.
The stability control feature works under all driving and
operating conditions. Under certain driving conditions, the ABS/TCS
function can be activated simultaneously with the ESP function in
response to a command by the driver.
In the event of a failure of the stability control function, the basic safety function, ABS, is still maintained.
Description of ESP Control
ESP system includes ABS/EBD, TCS and AYC function.
ABS/EBD function The ECU changes the active sensor signal (current shift) coming from the four wheel sensors to the square wave.
By using the input of above signals, the ECU calculates the
vehicle speed and the acceleration & deceleration of the four
wheels.
And, the ECU judges whether the ABS/EBD should be actuated or not.
TCS function prevents the wheel slip of drive direction by
adding the brake pressure and engine torque reduction via CAN
communication.
TCS function uses the wheel speed sensor signal to determine the wheel slip as far as ABS function.
AYC function prevents unstable maneuver of the vehicle. To
determine the vehicle maneuver, AYC function uses the maneuver sensor
signals(Yaw Rate Sensor, Lateral Acceleration Sensor, Steering Wheel
Angle Sensor).
If vehicle maneuver is unstable (Over Steer or Under Steer),
AYC function applies the brake pressure on certain wheel, and send
engine torque reduction signal by CAN.
After the key-on, the ECU continually diagnoses the system failure. (Self-diagnosis)
If the system failure is detected, the ECU informs driver of
the system failure through the BRAKE/ABS/ESP warning lamp. (fail-safe
warning)
Input and Output Diagram
| ESP Operation Mode |
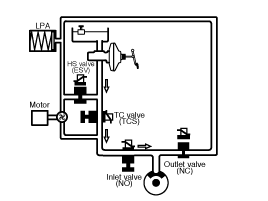
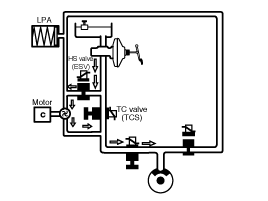
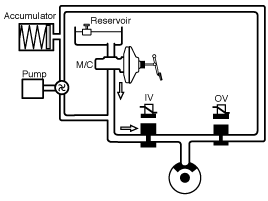
ESP Hydraulic System Diagram
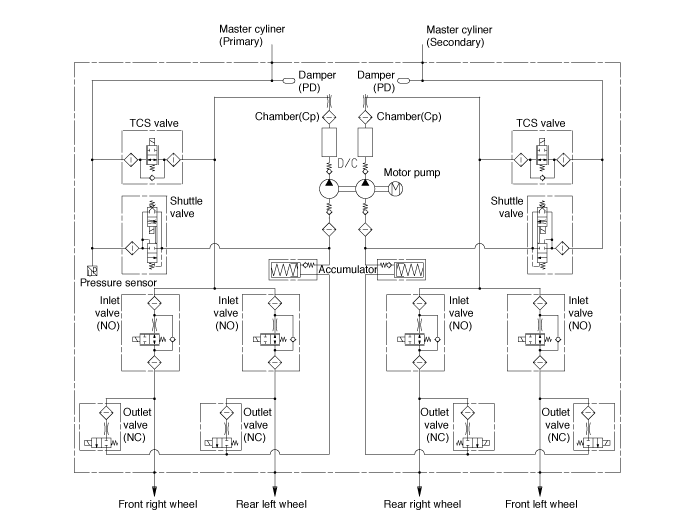
| 1. |
ESP Non-operation : Normal braking.
Operation
In this position, the inlet valve and the TCS valve are open,
the electrically operated shuttle valve and the outlet valve are
closed.
*ESV: Electric reversing valve.
|
| 2. |
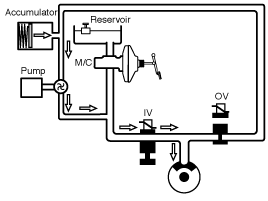
ESP operation
Operation
The on/off booster builds up a pressure of approx. 10 bar in
order to enable the ESP pump to suck brake fluid at low temperatures. In
this position, the inlet valve is driven in a pulsed cycle. The TCS
valve is closed. The outlet valve remains closed. The electrically
operated shuttle valve is opened. The hydraulic pressure is led to the
wheel brakes which are to be applied for a brief period of time.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
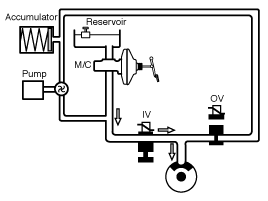
ABS Operation Mode
| 1. |
Normal Braking
When braking, the hydraulic pressure in the TMC is increased.
The pressure reaches the wheel brake via the current less open inlet
valve IV. The current less closed outlet valve OV is closed. For the
sake of simplicity the diagram is limited to only the solenoid valve
pair of one brake circuit. The wheel speed is reduced as the brake
pressure increases, in the extreme case until the wheel locks.
|
| 2. |
Dump Mode
If the wheel speed decreases, there is still a tendency to
lock; the brake pressure on the corresponding wheel must be reduced
accordingly. For this, the outlet valve OV is opened, the inlet valve IV
remains closed.
The brake pressure to the low-pressure accumulator is reduced. The wheel in danger of locking gains speed again.
|
| 3. |
Hold Mode
When a wheel (or several) tends to lock the inlet valve IV is
first closed to avoid a further increase in brake pressure. The outlet
valve OV remains closed: the brake pressure is kept constant.
|
| 4. |
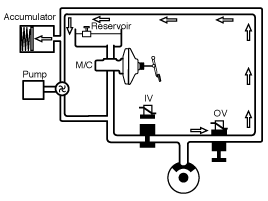
Increase Mode
For optimum brake from the certain wheel acceleration a brake
pressure increase is necessary. For this, the inlet valve IV is opened
and the outlet valve OV is closed. The pump of the unit starts to run
and aspirates the necessary quantity of fluid from the Low-pressure
accumulator, in order to produce the necessary brake pressure for the
pressure increase phase in seconds.
With an increase in the brake pressure the wheel speed is
reduced. These control phases are repeated until the ABS control unit no
longer detects any tendency of the wheels to lock.
|
ABS Warning Lamp Module

ABS Warning Lamp
The active ABS warning lamp module indicates the self test and failure status of the ABS .The ABS warning lamp shall be on:
| - |
During the initialization phase after IGN ON.
(Continuously 3 seconds). |
| - |
In the event of inhibition of ABS functions by failure. |
| - |
During diagnostic mode. |
| - |
When the ECU Connector is separated from ECU. |
EBD/Parking Brake Warning Lamp
The active EBD warning lamp indicates the self test and
failure status of the EBD. However, in case the Parking Brake Switch is
turned on, the EBD warning lamp is always turned on regardless of EBD
functions. The EBD warning lamp shall be on:
| - |
During the initialization phase after IGN ON.
(Continuously 3 seconds). |
| - |
When the Parking Brake Switch is ON or brake fluid level is low. |
| - |
When the EBD function is out of order. |
| - |
During diagnostic mode. |
| - |
When the ECU Connector is separated from ECU. |
ESP Warning Lamp (ESP System)
The ESP warning lamp indicates the self test and failure status of the ESP.
The ESP warning lamp is turned on under the following conditions:
| - |
During the initialization phase after IGN ON.
(Continuously 3 seconds). |
| - |
In the event of inhibition of ESP functions by failure. |
| - |
During diagnostic mode. |
ESP Function Lamp (ESP System)
The ESP function lamp indicates the self-test and operating status of the ESP.
The ESP Function lamp operates under the following conditions:
| - |
During the initialization phase after IGN ON.
(Continuously 3 seconds). |
| - |
When the ESP control is operating. (Blinking - 2Hz) |
ESP ON/OFF Switch (ESP System)
The ESP On/Off Switch shall be used to toggle the ESP
function between On/Off states based upon driver input. The On/Off
switch shall be a normally open, momentary contact switch. Closed
contacts switch the circuit to ignition.
Initial status of the ESP function is on and switch toggle the state.
AVSM OFF Lamp (AVSM System)
It is on cluster menu(UMS : User Menu Setting) turned ON when the driver select the "AVSM OFF" switch.
| Advance Vehicle Saftey Management(AVSM) |
Description
The AVSM is an electronic control system that can provide
vehicle stability, control car-to-car distance and offer parking
convenience through the integrated control of the damping, braking and
driving forces using the suspension system and the Smart Cruise Control
(SCC) system on the basis of Electronic Stability Program (ESP) system.
It consists of the high-performance Smart Cruise Control
(SCC), Pre-safe Seat Belt (PSB), and the cluster and warns the driver
with warning sound, warning lamp, and the belt vibration in accordance
with driving condition. When emergency condition, it can protect the
driver from critical injury by controlling the seat belt and brake.
| Components |
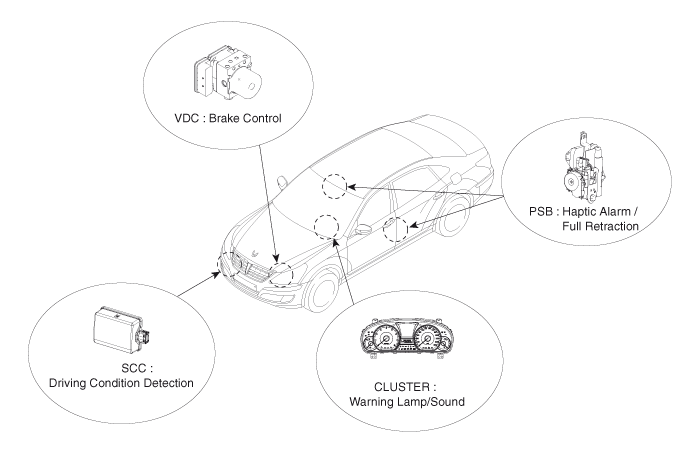
* VDC : Vehicle Dynamic Control
SCC : Smart Cruise Control
PSB : Pre-safe Seat Belt
 Components and Components Location
Components and Components Location
Components
1. ESP control module (HECU)2. Steering angle sensor3. Rear wheel speed sensor4. Sensor cluster (Yaw rate & Lateral)5. Front wheel speed sensor
...
 Schematic Diagrams
Schematic Diagrams
ESP Circuit Diagram
ESP Connector Input/Output
[Standard]
[Premium]
Connector TerminalSpecificationPin NoDescriptionStandardPremium2931IGNITION1(+)High level of wake up voltage : 4.5V < ...
See also:
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV) Repair procedures
Inspection
1.
Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2.
Disconnect the PCSV connector.
3.
Measure resistance between the PCSV terminals 1 and 2.
4.
Check that the resistance is within the speci ...
Interior light
CAUTION
Do not use the interior lights for extended periods when the engine is not
running. It may cause battery discharge.
WARNING
Do not use the interior lights when driving in the dark. Accide ...
Components and Components Location
Component Location
1. Horn switch2. Engine room relay box3. Horn (Low pitch)4. Horn (High pitch)5. Horn relay6. Clock spring
...
Categories
Hyundai Equus Manuals
© 2011-2025 Copyright www.heqmanual.com